What is an ecommerce SEO audit?
An ecommerce SEO audit aims to provide actionable insights into a business’ organic search performance. While every audit is unique, there are a core number of on-site and off-site considerations that should be covered, from crawlability to user experience. The scope of an ecommerce audit varies depending on the size of the site and the brief, so we have created a general checklist of areas to look out for below.
Ecommerce SEO Checklist
Technical SEO
The technical health of a site is a core pillar of an ecommerce SEO strategy. The foundations of organic search performance are built on the site being crawlable and indexable to search engines, requirements that are often not met if not regularly reviewed. Websites are also judged on their site speed and mobile-friendliness.
Indexation
The Coverage tab in Google Search Console provides a useful snapshot of indexability. The dashboard provides the list of URLs that Google has crawled and their status, whether they are Valid, Excluded or Erroring. You can then dig into the specific reason behind the status of each URL and take the necessary actions to fix any issues.
Crawler control
In order to maintain crawl efficiency and avoid content cannibalisation issues, it is important to manage how search engine bots crawl your site. This can be done in the robots.txt file of a site.
Site speed
The speed at which a site loads is a ranking factor in Google’s algorithm, which is why there are a plethora of site speed auditing tools available, including PageSpeed Insights. The tool provides a score for site speed on both mobile and desktop and recommendations on how to improve.
International setup
International ecommerce websites can encounter a number of technical SEO issues, including broken hreflang tags, incorrect canonicalisation and slow server response times. There are also considerations when it comes to having your international sites on subdomains, ccTLDs or as subfolders on a .com domain. Ensure you review each of these aspects in depth before launching into new markets. For more information, check out our extensive guide to international SEO.
Structured data setup
Schema markup helps search engines better understand the intent of the page and can even earn your pages rich results in Google. Product schema is one of the best types of schema to implement as it provides extra information on the price, availability and customer ratings for your products.
Core Web Vitals
The Core Web Vitals (CWV) were introduced as a ranking factor in June 2021. This set of metrics measure page experience metrics, including LCP, CLS and FID. Sistrix audited the impact of the algorithm impact and found a distinct difference in visibility for domains that performed well for these metrics and domains that performed badly. You can create your own dashboard to audit a site’s metrics for the CWV using a CruX dashboard.
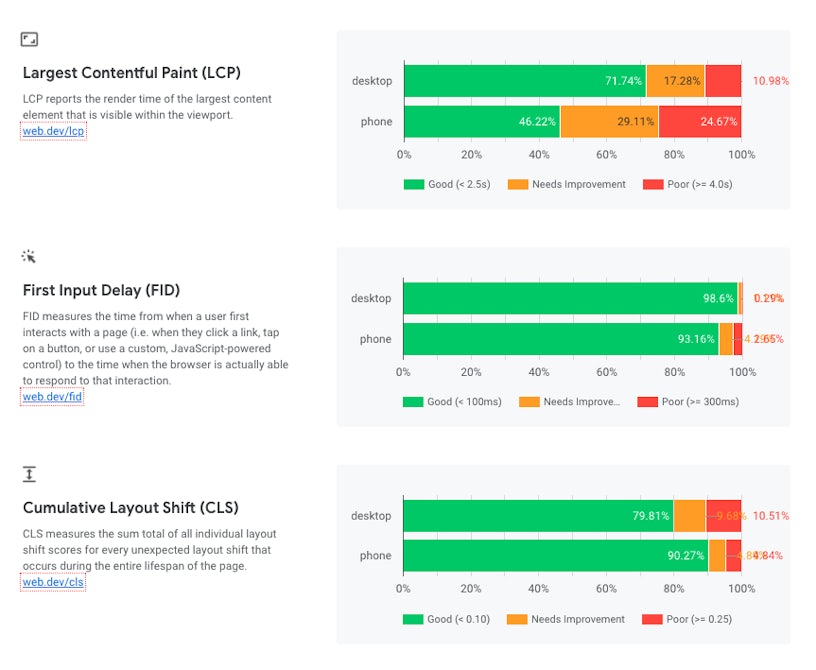
Mobile-friendliness
Mobile-friendliness is a key consideration for ecommerce SEO audits, as it is often the case that users will be browsing on their mobile devices rather than desktop. Google even uses mobile-first indexing, which evaluates the mobile-friendliness of the site as part of its ranking algorithm. Providing a great mobile experience is therefore paramount, and you can test this using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.
Content
Keyword targeting map
Carry out keyword research to understand how your target users are searching for your products or services and prioritise the queries with the most search volume. Then match the potential keywords to existing and future pages based on search intent in a keyword targeting map. This will then serve as the foundation of your content strategy.
Metadata
The title tag of the page is a ranking factor in search engine algorithms, so make sure to include the target keyword(s) wherever possible. The recommended title tag length is between 50-60 characters long as this is what Google usually shows in its results. Every page should have a unique title tag.
The meta description is not a ranking factor but should nonetheless be optimised because engaging descriptions increase the likelihood of someone clicking onto the page. Make sure to include a CTA in the description and aim for it to be between 130-160 characters long to fit within Google’s general guidelines.
HTML heading structure
Search engines reward pages that are well structured as it helps them assess the overall relevance of the page. Ensure that every page on your website has the appropriate HTML heading structure, especially the H1 tag. The H1 tag should include the page’s main target keyword to further help search engines understand the relevance of the page.
Content on category and product pages
Well-written content supports the keyword ranking potential of category and product pages. Write unique content for each category page describing the types of products the user will find within that category. Highlight any differentiating aspects of your products, and weave in your brand messaging to ensure a consistent experience across each page.
Cannibalisation
Ecommerce sites can sometimes suffer from multiple pages competing for the same query, otherwise known as keyword cannibalisation. This is most commonly found on product pages with similar features and dimensions. An ecommerce audit will identify how to best remove this cannibalisation to give the pages the best chance of ranking.
Informational content
Ecommerce sites should seek to gain visibility throughout the conversion funnel, not just for transactional keywords. Informational content can help boost brand awareness and provide useful answers to customers at the consideration stage of their journey.
User Experience (UX)
Internal site search
Site search is a powerful tool for ecommerce websites as it provides accurate data on the exact terms their customers are using to find their most desired products. This information can be used to identify potential blocks in the user journey, as well as which products to showcase more prominently on category pages and cross-sell modules.
Out of stock products
Managing out of stock products is an important consideration for both SEO and UX. Removing out-of-stock products can affect organic visibility by losing valuable backlink equity, while also representing a missed opportunity for upselling similar products. An ecommerce audit will outline how to manage stock availability at scale to encourage conversions.
Off-page considerations
Evaluating backlinks
Backlinks remain one of the most important ranking factors in Google’s algorithm, which means it is crucial for ecommerce sites to maintain a healthy backlink profile to remain competitive in the SERPs. Regular backlink health checks should be carried out to ensure identify any harmful links to the site and disavow them so search engines do not consider them.
Building backlinks
An ecommerce SEO audit will also scope out a layered link building strategy with op-level recommendations on how to build links, including broken link recovery, unlinked mentions and reactive comment opportunities. For a more comprehensive link building strategy, consult with a Digital PR agency.
Summary
If you would like expert advice on how to grow your ecommerce business without committing to a long term partnership, an ecommerce SEO audit is a great option. This guide outlines the initial checklist of areas that an audit will cover, and should give your team a good starting point of what you should be looking into.
If you would like to discuss the details of an ecommerce audit, our team is here to help. Get in touch with our team via email or over the phone to speak with one of our consultants.



